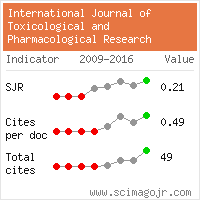
1. Analysis of Cost Variation among Different Brands of Fluoroquinolones Available in Indian Market – A Pharmacoeconomic Study
Rhythm, Sameer Pandit
Abstract
Background: Fluoroquinolones are one of the widely prescribed antibacterial agents in hospitals and community practices to treat infections all over the world. The lack of comparative information regarding cost variation among different brands of antibiotics puts the prescribers in a difficult state to choose the best medication and at the same time most cost-effective treatment regimen.
Aims and Objectives: The present study was done with the aim to evaluate the cost variation among the various brands of fluoroquinolones available in Indian market by calculating the percentage price variation.
Materials and Methods: CIMS (Current index of medical specialities) April to July 2022 edition was used to review the prices of different brands of oral and parenteral fluoroquinolones with same strength available in Indian market. Cost ratio and percentage price variation were calculated among different brands of fluoroquinolones.
Results: Maximum percentage price variation among oral fluoroquinolones of 2080.17 was found to be for levofloxacin 500mg which and the lowest percentage price variation of 66.67 was found to be for norfloxacin 200 mg. Maximum percentage price variation of 313.04 among parenteral fluoroquinolones was found to be for ofloxacin 200mg/100 ml and lowest of 59.89 was found to be for moxifloxacin 400 mg/100 ml.
Conclusion: The wide price variation between different brands of fluoroquinolones has been highlighted in our study. Physicians must consider socioeconomic background of patients should be considered while prescribing to reduce non-compliance and economical regimen for patients.
2. A Cross Sectional Survey on Self-Medication Practices during the COVID-19 Pandemic among the General Population in India
Anusha SJ, Padmaja Shetty K, Pratibha D Nadig
Abstract
Background: Self-medication(SM) trend has been reported to have increased worldwide due to a surge in the internet usage particularly during and after the pandemic. This global trend has posed a great challenge for clinical practice more so as there was a rise in the availability of new and repurposed pharmaceuticals.
Objective: 1) To assess the prevalence and pattern of SM during covid-19 pandemic among the general population. 2) To determine demographic variables and adverse events associated with SM. 3) To evaluate the drugs commonly used.
Materials and Methods: This pre-validated questionnaire-based cross-sectional survey was conducted between July 2021 to September 2021 on 400 subjects of the general population. The categorical variables were represented using frequencies and percentages. The chi-squares test used to see the statistical significant level and binary logistic regression were performed to determine the probable factors associated with SM practice.
Results: The study showed a prevalence of self-medication as 83% during Covid-19. There was also a significant increase in self-medication practice during the COVID-19 pandemic due to anxiousness (68.7%) among respondents. According to our results, 93% of respondents had heard about SM through pharmacist, the media, family, friends. Most commonly used drug was paracetamol primarily used for fever (76.2%).2.7% of respondents reported adverse events. SM practices were more among the females and employed individuals.
Conclusion: The study revealed the there was increase in the practice of SM during Covid time which was due to panic and anxiousness driven by wide media coverage on COVID 19, lockdown, restricted availability of medicines. This study has shown that there is a need for continued awareness and education about the risks of Self-medication.
3. Fetomaternal Outcome in Indoor Booked and Emergency Patients: A Prospective Observational Study
Hardik Bhikhalal Halvadia, Vipul S. Patel, Rajshree K. Modi, Manish Patel
Abstract
Background and Aim: Pregnancy is not a disease and pregnancy related morbidity and mortality are preventable. In view of current maternal mortality situation in India, it is pertinent to determine the relationship between the booking status of mother and maternal outcomes. Hence this study was aimed to determine maternal & fetal outcomes in Booked and Emergency patients.
Materials and Method: Booked patients are those who have ≥ 3 Antenatal visits, while Emergency (Unbooked) patients are those who had < 3 Antenatal visits. In my present study 500 patients were studied from August 2018 to July 2019 in department of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Among these 300 patients were Booked and 200 patients were Emergency patients (Unbooked).
Results: DIC, vaginal, cervical & perineal tear were slightly high in unbooked pts compared to booked patients. Cesarean hysterectomy was 3% in unbooked patients & 0.6% in booked pts. Wound gap was most common post partum complication which includes episiotomy and cesarean wound gap. Postpartum complications were more in unbooked patients compared to booked patients.
Conclusion: Most maternal and perinatal deaths are preventable if complications are diagnosed and managed effectively in time. Hence targeted, integrated, patient friendly, affordable and accessible health services need to be delivered in an equitable manner so as to improve the outcome for many antenatal patients.
4. A Single Centre Study of Recurrence in Phyllodes Tumour
Ashish Kumar Dubey, Sunil Kumar Saxena, Surendra Kumar Padarya, Shatkratu Dwivedi
Abstract
Background: Rare fibroepithelial neoplasms of the breast include phyllodes tumors. These constitutes less than 1% of all female breast neoplasms., Correct surgical planning and recurrence prevention are made possible by accurate preoperative pathological diagnosis. Treatment could be either lumpectomy or simple mastectomy to achieve histopathological clear margins. Due to the lack of knowledge regarding phyllodes tumors in general and in India in particular, the study’s goal included a detailed research analysis of cases and discussion of phyllodes tumour recurrence.
Materials and Methods: This study was a systematic retrospective record-based 3-year review of patient with phyllodes tumour admitted in department of surgery in a tertiary care institute was done from 2018-2021. Records were analyzed and researched with appropriate statistical methods.
Results: Nineteen (19) patients were enrolled in this study. There median age was 45 years., 16 patients were treated by lumpectomy, 2 patients treated by simple mastectomy & 1 patient by modified radical mastectomy i.e. 3 were observed with recurrence.
Conclusion: In present time, early diagnosis and aggressive surgical management is foremost the best treatment for Phyllodes tumour. This will require good reporting, compliance & multicentric studies globally.
5. A Comparative Study between the Efficacy of Clonidine and Dexmedetomidine Used as Adjuvant to Ropivacaine for Brachial Plexus Block by Supraclavicular approach for Upper Limb Surgery
Sudipta Mullick, Amitayu Nandi, Manisankar Nath, Purba Haldar, Mausumi Neogi
Abstract
Introduction: Peripheral nerve block of the upper extremity with local anesthetic agent along with analgesic adjuvant produce intense nerve block for surgical procedure and also produce good postoperative analgesia.
Aims & Objective: The objectives of this study were to compare the effects of Inj. Ropivacaine, Inj. Ropivacaine with Clonidine, Inj. Ropivacaine with Dexmedetomidine as adjuvants, used for Supraclavicular approach of brachial plexus block with respect to onset, duration of motor and sensory block, duration of analgesia and untoward side effects.
Methods: 40 patients were allocated in following groups and Brachial plexus block were administered in Group R with 0.5% ropivacaine (3mg/kg) + normal saline to make total 40ml volume, Group C with 0.5%ropivacaine(3mg/kg) + 1mcg/kg of clonidine + normal saline to make total 40 ml volume and Group D – with 0.5% ropivacaine (3mg/kg) + 1mcg/kg of dexmedetomidine + normal saline to make total 40ml volume. All demographic and Vital parameters of the patients. time of onset and duration of sensory & motor block and degree of sedation at intervals of 0, 5, 10, 20, 30, and 120 min were monitored.
Results: The onset of sensory and motor block was shortest in Gr D. The duration of sensory and motor block the duration of postoperative analgesia was longest in Gr D and shortest in Gr R. There was a significant difference in sedation score at 10 and 30 mins between Gr R and Gr C and also between Gr R and Gr D. There was no difference between Gr C and Gr D in sedation score.
Conclusion: Insupraclavicular brachial plexus block, adding Dexmedetomidine (1mcg/kg) as an adjuvant to ropivacaine (0.5%) results in faster onset and longer duration of sensory and motor block with longer duration of analgesia than the addition of clonidine.
6. Relationship between Stature and Arm Span among Adolescent Age Groups
Kamboj Kanwal, Sinha Amrita, Pandey Kuldeep
Abstract
Background: Generally it is not possible to measure stature of a person because of deformities of the limbs, in person who have undergone amputations or in cadavers where only parts of dead subject are available so stature has to be estimated.
Objectives: Estimation of stature from the arm span among adolescent age groups.
Material and Method: This cross sectional study was conducted on 150students of adolescent age groups from aged 10-18 years in one of the school of Kanpur City,India during August 2021 to January 2022. Out of 150, 78 were boys and 72 were girls. Analysis was done by using computer based program (SPSS).
Results: Strong correlation between height and arm span which was statistically significant. This was found to be 0.9313 in total subjects, 0.8061 in males and 0.8661 in females. Regression equations were derived and verified on subjects with known parameters using standard procedures.
Conclusion: Arm span is the most reliable body parameter for estimating the height of an individual with high accuracy.
7. Randomized Clinical Trial of Desflurane Vs Sevoflurane for Hemodynamic Stability and Recovery Profile in Laparoscopic Surgeries
Jigna R Shah, Apoorva R Moghe, Samarth P Gosai, Maulik D Humbal
Abstract
Background and Aim: Inhalational anaesthetic agents are used for maintenance of general anaesthesia. Sevoflurane and Desflurane have been in use for ambulatory anaesthesia as both have properties of an ideal agent. This study was carried out to compare the effect of sevoflurane and desflurane anaesthesia on emergence and extubation in laparoscopic surgeries.
Material and Methods: Present Randomized Control Trial was done at the Department of Anaesthesia, GMERS Medical college and hospital, Sola, Ahmedabad, Gujarat from July 2019 to June 2021. Simple randomization technique was employed using a computer-generated random number table and final sample size calculated was 68. Two groups were created by Randomized Computer Sampling method. GROUP D: Maintenance anaesthesia with desflurane. GROUP S: Maintenance anaesthesia with sevoflurane. Perioperative hemodynamic parameters were recorded. Postoperative recovery was assessed by the time from discontinuation of inhalational agent to response to painful stimuli, to spontaneous eye opening, to verbal commands, stating name, able to lift limb. Modified ALDRETE Score was recorded at the time of arrival to PACU.
Results: Intra-operative systolic and diastolic blood pressure and SpO
2 did not differ in both the groups during course of anesthesia. Patients in group D were responding to verbal command at an average 4.9 min as compared to 7.46 min in sevoflurane group. Time to achieve MODIFIED ALDRETE SCORE of 9 was faster in desflurane (9.14) group then sevoflurane (10.17) group. p<0.05, the difference is statistically significant. (p<0.05).
Conclusion: Both Desflurane and Sevoflurane provide stable intraoperative hemodynamic, but the main difference lies in their recovery profile. Desflurane is associated with faster and better recovery as compared to sevoflurane.
8. Comparative Assessment of the Thyroid Profile of Postmenopausal Women with Those in Reproductive Age Group: an Analytical Study
Prince Chandra Shekhar, Nimisha Priya
Abstract
Aim: The aim of the present study was to compare thyroid profile of postmenopausal women with those in reproductive age group as well as to find the correlation between age and thyroid profile.
Methods: The present study was conducted by the Department of Biochemistry, Shree Narayan Medical Institute & Hospital, Saharsa, Bihar, India, for the period of 1 year. The study includes 100 young and middle-aged pre-menopausal women (18-50 years) and 100 elderly post-menopausal women (>50 years). All the subjects enrolled in the study were female patients attending the outpatient department of the Hospital. Informed and oral consent was obtained from all the study participants and the study was approved by the institutional ethical committee.
Results: Post-menopausal women showed slightly increased TSH activity (3.39±2.45) as compared to pre-menopausal women (2.80±1.36). The activities of T3 and T4, however, revealed no variation among the study groups.
Conclusion: This demonstrates that for the purposes of thyroid-function screening in pre-menopausal and post-natural-menopause women, it suffices to measure the T4 and TBG levels and, obviously, the T4/TBG ratio. In view of the results obtained from the current research and considering the previous reports, there is a possibility of a shift in the activities of thyroid hormones with age.
9. A Prospective Observational Assessment of Cyto-Histopathological Correlation in Thyroid Lesions
Nivedita Singh, O.P. Dwivedi
Abstract
Aim: To correlate cytological and histopathological finding in thyroid lesions.
Material & Methods: This observational Prospective study was conducted in the Department of pathology, NMCH, Patna, Bihar, India, from February 2018 to January 2019.
Results: A total of 105 patients with thyroid lesions were subjected to fine needle aspiration cytology during a period of 1 year. Of these 42 patients underwent surgery
. In present study the cytology – histopathology concordance rate for non-neoplastic lesions is 89.0%.
Conclusion: By comparing the result of FNAC and histopathology, FNAC had higher accuracy, sensitivity of 80% and specificity 100% in the diagnosis of neoplastic thyroid lesions. FNAC is safe, inexpensive and less invasive diagnostic method with excellent patient compliance. FNAC can be used in the management of thyroid swelling to avoid unnecessary surgery on conditions like thyroiditis. FNAC with the help of imaging techniques is helpful in diagnosis of neoplastic lesion.
10. Comparative Assessment of the Fasting and Non-Fasting Lipid Profile in Healthy Adult Population: An Analytical Study
Prince Chandra Shekhar, Nimisha Priya
Abstract
Aim: The study was proposed to test the feasibility, of using non-fasting sample to estimate lipid profile, by comparing the lipid profiles obtained in fasting and non- fasting.
Methods: The present study was conducted by the Department of Biochemistry, Shree Narayan Medical Institute & Hospital, Saharsa, Bihar, India, for the period of 2 years.
Results: The lipid profile parameters in both groups in fasting and postprandial statuses were compared. In fasting group, the mean fasting serum total cholesterol level was 194.6 mg/dl and in postprandial group, mean serum total cholesterol level was 196.46 mg/dl (P = 0.0490). In fasting group, the mean fasting serum triglyceride level was 124.18 mg/dl and in postprandial group, mean serum triglyceride level was 127.19 mg/dl (P = 0.0001). The mean fasting High Density Lipoprotein (HDL) level was 47.09 mg/ dl and mean postprandial HDL was 45.90 mg/dl (P = 0.0798). The mean fasting serum VLDL level was 26.25 mg/dl and mean postprandial VLDL level was 27.34 mg/dl (P=0.0001). The mean fasting LDL was 124.6 mg/dl and mean postprandial LDL was 126.10 mg/dl (P = 0.0350).
Conclusion: We found that there is no significant clinical difference between fasting and non-fasting levels of total cholesterol, HDL, LDL, VLDL and TG. Thus, for estimation of lipid profile we can use the blood samples at any time or irrespective of mealtime.
11. Comparative Assessment of the Outcome of Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair and Open Incisional Inguinal Hernia Repair Surgery
Sanjay Kumar
Abstract
Aim: The present study evaluate and compare the outcome in terms of operative duration, post-operative pain, post-operative analgesic requirement, and post-operative complications between laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair and open incisional inguinal hernia repair surgery.
Methods: The present study was conducted in the Department of General Surgery, Sri Ramkrishna Institute of Medical Sciences and Sanaka, Hospital, Durgapur, West Bengal, for the period of 1 year . A total of 70 patients with uncomplicated inguinal small or medium sized, direct or indirect, unilateral or bilateral hernias undergoing elective inguinal hernia surgery, who are fit for laparoscopy and open surgery were included in the study. The study consisted of 70 patients, of which 35 were in the open surgery group and 35 were in the laparoscopic group.
Results: The study consisted of 70 patients, of which 35 were in the open surgery, while the other 35 were in the laparoscopic group. The open surgery group had patients with a mean age of 44.16±14.50years, with 25 males and 10 females. The laparoscopic group consisted of patients with a mean age of 46.67±19.21 years, with 28 males and 7 females. 59 of the cases presented with unilateral hernia, of which 38 showed right laterality and 21displayed left laterality. In 11 cases, bilateral representation was noted. 21 cases were of direct type, 36 of indirect type, and 13 of direct/indirect type.
Conclusion: Laparoscopic hernia repair is safe and provide less postoperative morbidity in experienced hands compared to open hernia repair.
12. Experimental Evaluation of Anti-Allergic, Antioxidant & Diuretic Activity in Vetiveria Zizanoides (Cleome Viscose) Roots in Rats
Dibyadeb Gosh, Irfan Ahmad Khan, Seema Singh
Abstract
Background: Cleome viscosa Linn. (Capparidaceae), popularly known as the “Asian spider flower”, is a native tree and found abundant in India. This study aimed to evaluate the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, and diuretic activity of the root extracts obtained from
Cleome viscosa using in vitro and in vivo experimental models.
Methods: The ethanolic extracts and its fractions obtained from
Cleome viscosa roots through Soxhlet extraction was analyzed by various activities. Different extracts were tested for total phenolic and flavonoid contents and in vitro antioxidant (ABTS & DPPH assay), anti-inflammatory (protein denaturation), anti-allergic (milk-induced eosinophilia), and diuretic (Lipschitz test) activities.
Results: Ethanolic extract exhibited the total phenolic (4.51±0.4) and flavonoid (5.34±0.93) content and highest antioxidant activity [{in ABTS (at 0.1 mg/mL; 33.62±0.76)} and {in DPPH (at 0.02 mg/mL; 29.30±0.56)} comparable to ascorbic acid, a standard compound {(0.04 mg/mL; 47.45±0.19) and (0.06 mg/mL; 97.14±0.53)} % inhibition] respectively. Whereas the 150 μg/mL dose of EECV shows 51.07±0.92 % inhibition and viscosity of 0.79±0.75 cp as compared to 625 μg/mL dose of Diclofenac sodium shows 56.23±1.98 % inhibition and viscosity 0.92±0.61 cp. Additionally, the total leucocyte count (at 100 mg/kg; 2483.34±148.14 per cu mm) and Eosinophils count (at 100 mg/kg; 66.6±10.54 per cu mm) was observed in anti-allergic activity when compared to the standard (Milk as 4 ml/kg; 3180.21±136.0 and 84.1±42.90) respectively. Also, diuretic activity was found significant in the petroleum ether fraction (200 mg/kg) as compared to the tested standard drug (Furosemide).
Conclusions: It can be suggested that
Cleome viscosa a great potential source of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic and diuretic compounds useful for new diuretic drugs from the natural basis.
13. Prospective Evaluation of Endoscopic Composite Cartilage Graft Tympanoplasty in Chronic Otitis Media Patients
Sanjeev Kumar
Abstract
Aim: To determine the functional outcome of endoscopic composite cartilage tympanoplasty in patients having chronic otitis media with safe central perforation (small or medium).
Methods: This prospective study was conducted on 100 chronic otitis media cases with safe central perforation (small/medium) in the Department of ENT, Lord Buddha Koshi Medical College & Hospital, Saharsa, Bihar, India for the period of 1 year. All the patients were selected as per the described inclusion and exclusion criteria. All cases underwent endoscopic composite cartilage graft tympanoplasty (type-I) under general anesthesia. Audiological outcomes were assessed by comparing mean pure tone average pre-and post-operatively and morphological results (successful graft uptake) were evaluated at 6 months.
Results: The result of this study showed graft uptake success in 94 case sand failure was seen in 6 cases. The pre-operative ACT was 44.8±6.1 dB whereas postoperatively it was 29.61±6.31 dB and the difference between the pre-operative and post-operative values was found to be statistically significant.
Conclusions: we conducted an endoscopic composite cartilage graft tympanoplasty (type-I) in 50 cases and observed a graft uptake success rate of 94%. There was good uptake of graft along with improvement in the audiological profile of the patients.
14. A Hospital Based Assessment of the Aetiology of Different Granulomatous Lesions: A Histopathological Analysis
Kumar Suneet
Abstract
Aim: To analyze different granulomatous lesions and to find the frequency and etiology of all granulomatous lesions.
Materials and Methods: The present observational study was carried out in the Department of Pathology, Lord Buddha Koshi Medical College & Hospital, Saharsa, Bihar, India for the period of 1 year. We include 100 cases of skin biopsies after histopathological confirmation of granulomatous lesions.
Results: Among 100 cases were studied in which male predominance was noted with 60(60%) cases and females constituted 40(40%) case providing M :F ratio of 3:2. Most of the patients were noted in age group of 20 to 30 years i.e 36(36%) cases followed by 21(21%) case in 30 to 40 years. 83% of cases were seen below 50 years of age in our study. Infectious granulomatous dermatoses were very common, only 1 cases of sarcoidosis was found. Most cases of infectious dermatoses were noted in 20 to 30 years comprising 36(36%) cases. Leprosy remained the significant causative reason for infectious granulomatous dermatoses succeeded by tuberculosis of skin. Borderline tuberculoid leprosy was found to be predominant, constituting 27 (27%) cases followed by indeterminate and lepromatous leprosy both had 22(22%) cases, tuberculoid leprosy 18(18%) case and 8(8%) of borderline lepromatous. Lupus vulgaris constituted 1 cases (1%) and only 1 (1%) case of sarcoidosis was found.
Conclusion: The granulomatous lesion is common in third decade of life with male predominance. Leprosy was the most common cause of cutaneous granuloma followed by Tuberculosis, fungal infection and foreign body reaction.
15. A Retrospective Study to Establish How Useful Mammography and Sonography Was in Confirming the Diagnosis
Archana Kumari
Abstract
Aim: This study is done to establish how useful mammography and sonography was in confirming the diagnosis.
Methodology: A retrospective study was undertaken of all patients presenting to Department of Radiology, ICARE Institute of Medical Sciences and Research & Dr. Bidhan Chandra Roy Hospital, Haldia, West Bengal, India for 1 year.whose core biopsy (CB) revealed a diagnosis of fat necrosis. The presenting symptoms, including any history of trauma, were noted. The clinical examination findings were also reviewed. The interpretation of each clinical, mammographic and ultrasonic examination was prospectively classified using a four category scale (1 ¼ normal, 2 ¼ probably benign, 3 ¼ possibly malignant and 4 ¼ probably malignant). Ultrasound findings were sub grouped into (i) depth within the breast tissues planes, (ii) purely solid lesions, (iii) purely cystic lesions, (iv) complex lesions, (v) the transmitted sound characteristics, (attenuation, enhancement), or (vi) normal examinations. Mammographic findings were categorized as (i) well or poorly defined lucencies, (ii) well or poorly defined densities, (iii) parenchymal disturbances, (iv) skin thickening, (v) related or distant calcifications and (vi) normal study.
Results: All 50 patients presented with a palpable abnormality, 48 were discrete masses while 2 demonstrated generalized segmental nodularity. The patients’ ages ranged from 28 to 75 years (mean 55.4 years). Only 26 (52%) of the 50 cases had a clear history of trauma or demonstrated definite signs, e.g. scar or bruising, to suggest trauma. 19 (38%), lesions were tender. 28 (56%) lesions were associated with bruising at various stages of evolution. 3 (6%) lesions had associated skin dimpling. The mean time from recalled trauma to presentation and imaging was 8.43 weeks. Mammography was performed in 100% of the patients. 27 (54%) of the mammograms were normal. The Wolfe pattern characteristic was grouped as follows: N1 type ¼ 23, P1 type ¼ 8, P2 type ¼ 19, DY type ¼ 0. All 50 ultrasound examinations revealed a visible abnormality corresponding to the site of clinical concern. The lesions were distributed within the breast tissue as follows: (i) 10 lesions (20%) within the superficial subcutaneous tissue of the skin and fatty tissue; (ii) 33 (66%) lying deeper, purely within fatty tissue; (iii) 7 (14%) lying deeper within fat and glandular tissue. The size of the lesions ranged from 5 to 21 mm, mean 13.3 mm.
Conclusion: From this study, it can be concluded that when clinically fat necrosis is suspected, the mammogram and ultrasound are the most important diagnostic tools. If there are no suspicious features of malignancy on the mammogram, then USG appearances can be relied upon to give a diagnosis of early fat necrosis.
16. Etiological Assessment of Urinary Bladder Carcinoma in Patients Presenting to Tertiary Care Centre
Jitendra Kumar
Abstract
Aim: The aim of this study was to determine the etiological of urinary bladder carcinoma patients.
Material and methods: This Prospective observational study was done in the Department of General Surgery, ICARE Institute of Medical Sciences and Research & Dr. Bidhan Chandra Roy Hospital, Haldia, West Bengal, India for the period of 1.5 years. Total 200 patients with a diagnosis of bladder cancer were included in the study. Clinical details including history of hematuria, smoking, daily fluid intake, dietary history, symptoms of urinary tract infection (UTI), loss of weight/appetite, past medical history and blood tests including hemogram, renal function tests, liver function tests, imaging like ultrasonography of kidney, ureter, urinary bladder (USG KUB), contrast enhanced computed tomography of kidney, ureter, urinary bladder (CECT KUB) (if needed) and chest X-ray (CXR) was done in all the patients as per the standard protocol in the Department of General Surgery, ICARE Institute of Medical Sciences and Research & Dr. Bidhan Chandra Roy Hospital, Haldia, West Bengal, India.
Results: The mean age of presentation of carcinoma urinary bladder was 54.26 years. The male to female ratio was 4:1. The mean age of presentation of carcinoma urinary bladder was 54.26 years (29-84 years) with the maximum number of patients being in the age group of 60-70 years followed by below 40 years. 90% of the patients of carcinoma urinary bladder in our study were non-smokers. History of UTI was present in only 25.5% of the patients of carcinoma urinary bladder. Maximum number of patients of carcinoma urinary bladder belonged to A+ blood group followed by B+ and the least number of patients belonged to O- blood group. The maximum number of patients of carcinoma urinary bladder was labourers by occupation followed by farmers and housewife in females’ subset. As shown in the table the maximum number of patients of carcinoma urinary bladder was Hindus followed by Muslim.
Conclusion: we concluded that the majority of the patients turned out to be non-smokers and A +ve blood group in contrast to the strong predilection of smoking and bladder cancer.
17. A Hospital Based Outcome Assessemt of Laproscopic Verses Open Appendectomy
Perwez Alam Khan
Abstract
Aim: The aim of the study was to assess technical feasibility and safety of the laparoscopic technique in acute appendicitis and compare its results with open appendectomy.
Methods: The present study included Department of General Surgery, Lord Buddha Koshi Medical College & Hospital, Saharsa, Bihar, India. 50 patients presenting with clinical diagnosis of appendicitis. In order to compare the two techniques, patients undergoing LA were compared to patients undergoing OA over a period of 12 months. Those patients were excluded who had perforated appendicitis. Study to be carried out over a period of 12 months includes patient diagnosed with appendicitis and admitted to surgery ward at Department of General Surgery, Lord Buddha Koshi Medical College & Hospital, Saharsa, Bihar, India and enrolled in the study after obtaining the valid written informed consent.
Results: The maximum number of cases was observed in the age group of 25-36 years with a female (27) to male (23). The average age of patients undergoing LA was 26 years while it was 26.52 years for those undergoing OA. The mean operative time for the open appendectomy was 46.6 minutes and in laparoscopic appendectomy was 65.6 minutes. The difference between the two groups was significant, with a p-value of <0.001.
Conclusion: Laparoscopic appendectomy is better than open appendectomy with respect to wound infection rate, early resumption of oral feeds, lesser postoperative pain, postoperative hospital stay and return to normal activities. Though the mean duration of operation was more in the LA group, it can be considered as gold standard surgical treatment for the management of acute appendicitis.
18. Quantitative Assessment of the Parenchymal Thyroid Diseases using Multiparametric Ultrasonography
Archana Kumari
Abstract
Aim: To assess some quantitative spectral Doppler parameters, resistivity index (RI) and acceleration time (AT) together to show their reliability for differential diagnosis of parenchymal thyroid diseases.
Methods: This study was conducted in the Department of Radiology, ICARE Institute of Medical Sciences and Research & Dr. Bidhan Chandra Roy Hospital, Haldia, West Bengal, India, for the period of 1 year. Patients were divided into five groups such as group I (normal); group II had first detected, early untreated Hashimoto disease (EH); group III comprised of chronic Hashimoto patients that are under treatment and/or follow up (H); group IV had multinodular parenchymal hyperplasia (M); and group V had nodular hyperplasia with Hashimoto (HM). They underwent spectral Doppler ultrasound and acoustic radiation force impulse using Siemens ACUSON S2000 machine. Quantitative spectral doppler parameters such as resistivity index (RI) and acceleration time (AT) was recorded.
Results: Out of 200, 62.5% were male and 37.5% female most of the patients between 30-40 years 42.5% and followed by 40-50 years was 30%. The Distribution of patients based on diseases and each group had 40 patients. The mean RI in group I was 0.57, in group II was 0.60, in group III was 0.45, in group IV was 0.51 and in group V was 0.53. Mean AT in group I was 25.9, in group II was 24.8, in group III was 69.5, in group IV was 45.8 and in group V was 44.5. The difference was significant (P< 0.05).
Conclusion: The resistivity index and acceleration time together are reliable for differential diagnosis of parenchymal thyroid diseases.
19. A Clinicopathological Profile of Benign Breast Diseases in Women
Jitendra Kumar
Abstract
Aim and objective: Aim of this study was to evaluate the clinicopathological profile of benign breast diseases in women.
Methods: A Prospective study was conducted in the Department of General Surgery, ICARE Institute of Medical Sciences and Research & Dr. Bidhan Chandra Roy Hospital, Haldia, West Bengal, India for the period of 1 year. Patients presented with different breast related problems like lump in breast, nipple discharge, associated fever and mastalgia were admitted in surgical ward for evaluation.
Results: In the present study, 120 cases were examined and analysed. Fibroadenoma formed the most common benign breast disease accounting for 50 cases (41.67%), followed by fibroadenosis in 25 cases (20.83%). Benign breast disease was commonly seen in the age group of 20-30years constituting 47.5% of all patients followed by 26.67% cases in age group of 30-40years. It is extremely uncommon in <10yrs and above 55years. Among all the benign breast diseases, left sided breast involvement was more common onstituting 62 (51.67%) cases while right breast involvement was less common constituting 45 (37.5%) patients. Bilateral involvement was seen in only 13 (10.83%) patients. Considering the pattern of benign breast diseases, fibroadenoma was the most common lesion constituting 50 (41.67%) cases followed by fibroadenosis (fibrocystic disease) constituting 25 (20.83%) cases, fibroadenoma with fibrocystic changes constituting 17 (14.17%) and breast abscess constituting 8 (6.67%) cases. Other benign breast diseases include phylloides tumour 5 (4.17%), lipomas 3 (2.5%) and 2 (1.67%)galactocele. Patients with breast lump 83.33%, patients with breast pain 35% and patients with nipple discharge 3.33%.
Conclusions: The breast lesions pattern revealed by the present study provides valuable information regarding clinicopathological profile of breast lesions.
20. A Hospital Based Clinical Assessment of the Efficacy of Nutraceuticals in the Management of Osteoarthritis
Varun Kumar
Abstract
Aim: The aim of the present study was to evaluate the marketed product TriNyros (combination of Rosehip, IridoForceTM, Aflapin) (Nutragenix Healthcare Pvt. Ltd.) as an additive treatment in OA patients and its effect in patients with & without comorbidity.
Methods: A phase IV post marketing surveillance study of Cap. TriNyros (Nutragenix Healthcare Pvt. Ltd.) was conducted at Department of Orthopaedics, Lord Buddha Koshi Medical College & Hospital, Saharsa, Bihar, India for 2 years. During the study total 160 patients were selected based on inclusion and exclusion criteria in which comprises 60 (37.5%) males and 100 (62.5%) females. The mean age of the subject was 58.60 years, and 70% patients belong to the age group above 50 years. Out of 160 patients, 75% patients had comorbidities such as hypertension, anxiety, diabetes mellitus, thyroid disorders etc. All the subjects selected during the study received TriNyros capsule two times daily for three months.
Results: During analysis of clinical symptoms parameters such as joint line tendinitis on palpations, limitation of mobility, joint crepitus, swelling and redness were included in the study. The treatment with TriNyros for 3 months leads to 60.64% reduction in pain on palpations of OA patient. Movement of a joint affected by OA may cause a crackling or grating sensation called “crepitus”. The reduction rate for joint crepitus is similar in OA patient with comorbidity (72.65%) & without comorbidity (66.70%).
Conclusion: OA as it has an important effect on the treatment. Finally, only one fixed dose of TriNyros was used during the study to evaluate its efficacy; hence we could not validate effect of different doses on safety and efficacy in OA patient. The findings of the current phase IV post marketing surveillance suggest that TriNyros (Nutragenix Healthcare Pvt. Ltd) act synergistically to exert anti-inflammatory/anti-arthritic activity. Cap TriNyros efficaciously reduces joint pain and improves the physical functional ability of OA patient.
21. A Hospital Based Retrospective Assessment Correlation between the Clinic-Pathological Factors and Gastric Cancer
Kumar Suneet
Abstract
Aim: To find correlation between clinical and pathological factors of gastric cancer in Bihar region, India.
Material and methods: This retrospective study was carried out Department of Pathology, Lord Buddha Koshi Medical College & Hospital, Saharsa, Bihar, India, for the period of 1.5 year. The study includes total 300 patients who fulfilled the inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Results: Of these 300 patients, 185 (61.7%) underwent distal gastrectomy, 12 (4%) proximal gastrectomy via abdomen and 72 (24.0%) via thorax, and 31 (10.3%) underwent total gastrectomy. Distal and total gastrectomy had more numbers of clearances of lymph nodes than the other operational approaches. The postoperative complications occurred in 26 patients 8.7%. The overall mortality was 2 (0.66%). patients 8.7%. The overall mortality was 2 (0.66%). Multiple regression analysis demonstrated that sex, location of tumor, tumor diameter, depth of tumor invasion and differentiation play an important role in the metastasis of lymph nodes.
Conclusion:This retrospective study has shown that clinicopathological characters in gastric cancer varied with sex, location, and diameter of the tumor.
22. A Hospital Based Cross-Sectional Assessment of the Risk Factors of Hearing Loss in Systemic Hypertension Patients
Sanjeev Kumar
Abstract
Background: To find out risk factors of hearing loss in systemic hypertension patients.
Methods: This is a hospital based cross-sectional study conducted in the Department of ENT, Lord Buddha Koshi Medical College & Hospital, Saharsa, Bihar, India. A sample of 140 hypertensives was studied. They were subjected to pure tone audiometry after detailed history and physical examination including recording of blood pressure.
Results: Out of the 100 hypertensives, 60 patients were detected to have sensorineural hearing loss. In our study, age, stage of systemic hypertension and duration of systemic hypertension were the risk factors found to be associated with sensorineural hearing loss.
Conclusions: In our study we have identified a high prevalence of sensorineural hearing loss in patients with systemic hypertension. Age, duration and stage of systemic hypertension were found to be risk factors for hearing loss in the study population.
23. To Estimate the Incidence of Intradialytic Hypotension in End Stage Renal Disease on Maintenance Hemodialysis and its Correlation with Serum Albumin – A Cross Sectional Study
Ajay Thobde, Sunita Gupta
Abstract
Background: Intradialytic hypotension (IDH) is considered one of the most frequent complications of haemodialysis treatment and is associated with increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Low serum albumin level frequently documented in the hemodialysis patients, but only few studies were done about the correlation of the serum albumin level and blood pressure changes during hemodialysis, so we planned this study to find out the incidence of intradialytic hypotension during haemodialysis & its correlation with serum albumin level.
Material and methods: 100 patients who have age 18 years and above with diagnosis of chronic kidney disease with end stage renal disease on maintenance hemodialysis thrice weekly, were taken from the dialysis unit after informed consent and after fulfilment of inclusion and exclusion criteria. Blood pressure monitoring was done every 30 min of interval in all subjects for 1 session of the hemodialysis over 4 hours. Biochemical parameters were measured in enrolled subjects before undergoing for the hemodialysis such as, serum albumin, serum creatinine, blood urea, serum sodium, serum potassium. Along with that interdialytic weight gain, blood flow, dialysate flow was also monitored.
Results: 31% subjects had significant fall in BP. Age, gender, associated comorbidities, duration of hemodialysis, blood urea, serum creatinine, serum sodium, blood flow, dialysate flow, interdialytic weight gain (IDWG) had no statistically significant correlation with the intradialytic hypotension (IDH). Mean serum potassium level was increased in IDH group with P value 0.039. Mean serum albumin level in IDH group was decreased with p value 0.003. In IDH group low mean serum albumin and high mean serum potassium level was observed.
Conclusion: We concluded that, incidence of IDH in chronic kidney disease with end stage renal disease on maintenance hemodialysis is 31%. Low serum albumin level and high serum potassium level are a better predictor of the IDH.
24. To Study the Histopathological Spectrum of Benign, Premalignant and Malignant Lesions of Prostatic Specimen Received in a Tertiary Care Center
Mitesh Shah, Rajesh Gaur, Ruchi Agrawal, Santosh Kumar Gond, Atul Jain, Shatkratu Dwivedi
Abstract
Background: Worldwide Prostate gland diseases were responsible for significant morbidity and mortality among adult males. Data available on prostate cancer showed significant difference in incidence, precipitating factors and disease characteristics of prostate cancer in India.
10 Thus, present study was conducted as an effort to assess histopathological spectrum of benign, premalignant and malignant lesions of prostatic specimen received in the Department of Pathology in Gwalior region through a hospital-based study.
Materials and Methods: This study was conducted in Department of Pathology, Gajra Raja Medical College and J.A. Group of hospitals, Gwalior (M.P.) from 1
st January 2016 to 31
st August 2017. Histopathological examination of all prostate samples received during this period was done after H & E staining.
Results: Total BPH cases were 89, 80.2% of all cases. 56 cases (50.4%) were associated with prostatitis while 33 cases (29.7%) were without prostatitis. Chronic prostatitis associated with BPH in 55 cases (49.5%) while in 1 case of BPH (0.9%) is associated with Granulomatous Prostatitis. There were 2 cases of Chronic prostatitis, comprising 1.8% of all prostatic cases. Pre-malignant lesions were 3 cases of Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia, 2.7% of all cases. All malignant lesions were Adenocarcinoma of prostate, total 17 cases were found, comprising 15.3% of all prostatic lesions.
Conclusion: Histopathology is an important tool to diagnose prostate lesions. Though predominant lesion is benign, sometimes carcinoma of prostate is incidental and in lower istological grade should be combined with immunohistochemistry for more definitive diagnosis.
25. Drug Utilization Study of Anti-Epileptic Drugs in Pediatric Population at Tertiary Care Hospital
Keshav Bansal, Dhaval Bhatt, Viswanadhula S L V Bhargav, Pranav Punasanvala
Abstract
Background: Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder that requires therapy over prolonged period of time to keep patient seizure free. Although patients respond with Monotherapy, refractory epileptic patients require Polytherapy. Drug utilization studies provide insight to rational drug prescribing.
Aim and Objective: To study prescription and drug utilization pattern of antiepileptic drugs in pediatric patients with epilepsy in a tertiary care hospital.
Materials and Methods: It is a retrospective study based on data collected from medical records and prescriptions of all epileptic pediatric patients. The data were collected in study pro forma and analyzed.
Results: Total of 162 patient’s details was collected retrospectively from the hospital outpatient department and inpatient department. In the present study, out of 162 patients, 102 (62.96%) patients were under 6 years of age (46 males and 56 females) and 60 (37.03%) patients were above 6 years of age (22 males and 38 females). Among all the patients, the most common type of epilepsy diagnosed in all the age groups was generalized tonic-clonic seizure (GTCS) contributing to 69.13%. The present study data of 162 patients’ revealed that the majority of the patients were receiving monotherapy with various drugs contributing it to 61.11%. About 38.88% of our study patients received polytherapy. Sodium Valproate (38.27%) was the most commonly prescribed drug as monotherapy and levetiracetam + sodium valproate (29.62%) for polytherapy.
Conclusion: Our study on drug utilization in pediatric epilepsy in a tertiary care hospital showed that the higher incidence of epilepsy is noted in females. GTCS was the most common type of epilepsy diagnosed and majority of the patients were prescribed with monotherapy with both conventional and newer antiepileptic drugs. Sodium Valproate was the most commonly prescribed drug as monotherapy and Levetiracetam and Sodium Valproate combination was most commonly used in polytherapy.
26. Immunomodulation During Hepatoprotective Effects of Dawa-Ul-Kurkum in D-Galactosamine- Induced Liver Cirrhosis in Rats
Mohd Rafi Reshi, Kavita Gulati, Arunabha Ray
Abstract
Background: The immunomodulatory and hepatoprotective effects of Unani preparation were evaluated in an experimental model of liver cirrhosis induced by administration of the D-galactosamine in rats.
Methods: Rats were administered with D-galactosamine, three times in a week (on alternate days) to induce hepatic derangement for about 06 weeks. The model of liver cirrhosis was confirmed by observation of alterations in various cytokines and markers of immunity as compared to that in vehicle control rats. The effects of Dawa-ul-kurkum and its hydro-alcoholic extract were evaluated on markers of immunomodulation and liver injury in the above model of liver cirrhosis in rats.
Results: D-galactosamine-induced liver damage was associated with higher levels of inflammatory cytokines, IgG, MDA, and NOx, as well as lower levels of GSH and a delayed-type hypersensitivity response, as compared to that in normal controls. Histopathological examination of liver tissue also revealed hydropic degeneration, chronic inflammatory cells, and partial septal cirrhosis in this experimental group. Treatment with Dawa-ul-kurkum and its hydroalcoholic extract evoked varying degrees of modulation of several cytokines, immunoglobulins, delayed-type hypersensitivity, and oxidative stress indicators and provided protection against deranged liver functions. The treatment with Unani polyherbal preparation and its extract had immunomodulatory effects similar to those seen with positive control (silymarin).
Conclusion: The results showed that both Dawa-ul-kurkum and its extract had hepatoprotective and immunomodulatory effects against liver cirrhosis induced by D-galactosamine in rats and the effects were comparable to those seen with silymarin.
27. To Assess the Functional Outcome of Intertrochanteric Fractures of Femur Treated with Proximal Femoral Nail
Manish Rajpoot, Sourabh Sharma, Suresh Uikey, Chetan Solanki, Gopala Rao Mundlapati
Abstract
Background: Intertrochanteric fractures occurs in the old aged after accidental fall due to osteoporosis and poor bone quality but in young individuals, these fractures are the result of road traffic accidents. Interestingly these constitute around 34% of all hip fractures. The calcar decides the stability of these fractures. Fixation needed in these fractures for early mobilization and better functional outcome. The focus of surgical research in these fractures is to reduce implant failure and cut out of the femoral head and neck fixation components. The current practice of treatment of a stable variety of intertrochanteric fracture with dynamic hip screw is widely accepted, however, an unstable variety of intertrochanteric fractures are better treated with Cephalo-medullary nails.
Materials and Methods: It’s a prospective study with a sample of 20 patients with Intertrochanteric fractures of the femur done in the Gandhi Medical College, Bhopal from July 2019 to june 2021. Operating time was calculated from the start of surgical incision to wound closure. Intra-operative blood loss was calculated from the number of mops and gauze piece soaked with blood. Patients were evaluated clinically and radiologically during follow up. Harris Hip Score (HHS) was calculated with the standard scoring sheet.
Results: Patients were evaluated clinically and radiologically at 3 weeks interval for first 3 months and there after monthly for the next 3 months and bimonthly for next 6 months. During follow up the Harris Hip Score was evaluated at 3 months and 6 months post operatively. Operating time varied from 58 to 84min. Blood loss varied from 150 to 350ml. The mean Harris hip score at the end of 3 months was 78.65 and at end of 6 months was 85.05. 1 patient had cutout of the cervical screws leading to collapse and severe varus deformity and another patient with a single load bearing cervical lag screw developed varus deformity. 3 patients developed abductor lurch which improved with time. Superficial wound infection occurred in 1 case and there were no cases of deep infection.
Conclusion: PFN has advantages of closed reduction, preservation of fracture hematoma, less tissue damage & minimal blood loss during surgery, Shorter operative time and early rehabilitation in the management of intertrochanteric fractures. The incidence of perioperative and postoperative femoral shaft fractures in PFN can be reduced by good preoperative planning.
28. ADR Profile of Covishield and Covaxin among Young Adults (18-45 Year) in a District in Northern India: A Comparative Study
Deb T, Beniwal A, Kamra N, Kaur M
Abstract
Background: The Covid-19 vaccines: Covishield and Covaxin have been approved by the Govt. of India for emergency use against SARS COV-2 virus. The vaccination drive was initiated on 16 Jan 2021 among healthcare workers. Following this, age groups above 45 years and people with co-morbidities were covered. On 1st May 2021, the vaccination drive was extended to cover young adults (18-45 years).
Objective: To evaluate Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) profile of Covishield and Covaxin among young adults (18-45 years) in Karnal district, Haryana.
Methods: A
descriptive cross-sectional study was performed for 2 months at the ADR Monitoring Centre located at Kalpana Chawla Government Medical College (KCGMC), Karnal, Haryana, India. ADRs of both vaccines (Covishield and Covaxin) among young adults (18-45 years) voluntarily reported at the ADR-monitoring centre from various vaccination centres of Karnal District, by healthcare workers or beneficiaries were recorded and selected for the study.
Results: One hundred and eleven ADRs were reported amongst 51 beneficiaries (85 ADRs among 38 Covishield vaccinated beneficiaries and 26 ADRs among 13 Covaxin vaccinated beneficiaries). There was no significant difference in the numbers of ADRs reported among males and females in both vaccine groups during the study period. The common ADRs reported in both vaccine groups were fever followed by body ache. One serious ADR was reported, which required admission in the hospital but was discharged on the same day. The majority of the suspected ADRs were classified as ‘Probable’ as per the WHO-UMC scale.
Conclusion: Among both the vaccine beneficiaries, no event of death or disability was reported. Common ADRs observed were fever, body ache, and weakness. There was no significant difference in the number of ADRs reported in the two vaccine groups.
29. Impact of Coronavirus Disease (Covid-19) Pandemic and Lockdown Over the Pattern of Hospitalisation, Surgical Burden and Changes in the Surgical Practices
Jitendra Singh Yadav, Khushal Rao Hurmade, Gajendra Dandotiya, Shashank Singh Baghel
Abstract
Objective: To quantify the impact of Coronavirus disease (
COVID-19)
pandemic and lockdown over the pattern of hospitalisation surgical burden and changes in the surgical practices of patients at department of General Surgery, MY Hospital, Indore.
Methods: Data pertaining to the hospital admission in department of surgery, MY Hospital, Indore during the period of 25th March till 14th April 2019 and between January 1, 2020 to June 30, 2020 was collected and evaluated for multiple parameters like the duration and cause of admission in the hospital, treatment offered and outcomes. This data was thoroughly assessed and looked for the differences in monthly hospitalisation, disease specific hospitalisation rate, mortality status and other parameters during precovid, covid and post covid era.
Results: During covid phase, discharge percentage decreased from 74.70 % to 39.47 %, the LAMA percentage rose from 12.47 % to 31.58 % and death percentage increased from 12.65 % to 27.63 %. The emergency admissions were the major indications for admission during both the phases, however elective admissions fell from 233 (39.89 %) in the non-lockdown phase (2019) to 0 in the lockdown phase (2020). The percentage of non-referred patients increased during the lockdown phase (2020). The difference between the two groups was not found to be statistically significant. Overall conservative management was the most commonly followed approach in both the phases. The percentage of conservative management increased from 42.90 % during the Non-Lockdown phase (2019) to 73.68 % during the lockdown phase. All surgeries performed during the Lockdown 01 Phase were emergency surgeries.
Conclusion: The other changes in the surgical practices within the Department of Surgery included significant decrease in the number of elective admissions and elective surgeries, increased preference for conservative management over surgical management, increased preference for regional anaesthesia, a decreased mean duration of stay for a patient in the hospital. Changes noted in surgical practices also included significantly reduced number of laparoscopic procedures. These changes appear to be a response towards the COVID 19 pandemic to prevent the spread of infection within the hospital as well as an attempt to secure the healthcare resources for the mitigation of ongoing COVID 19 pandemic.
30. An Investigation- Association of Sociodemographic Variables with The Practice of Self – Medication among Non- Teaching Staff in a Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital of Northern Haryana
Jayant Kumar Kairi, Manmeet Kaur, Amit Kaushik
Abstract
Background: Self-medication is a common practice. Most of the time no serious harm occurs. But sometimes it can be dangerous. It seems natural and logical that the staff working in close proximity to the indoor patient departments (IPD) and outdoor patient departments (OPD) should be able to consult the doctors easily. But a preliminary look at the Outdoor patient department (OPD) registrations were indicative of the trend that there were fewer registrations from the non-teaching staff of our college. We hypothesized that the reason could be self-medication. Furthermore, we could not find any study that investigated the pattern of self-medication in persons working in or in close proximity of a hospital The present study was planned to determine the extent and understand the various aspects of the practice of self-medication among the non-teaching staff.
Aims and Objectives: To determine the pattern of self-medication amongst the non-teaching staff at a tertiary care teaching hospital in Northern Haryana and to document the factors that motivate them to self-medicate.
Methods: The data on self-medication was acquired using a self-designed validated questionnaire. Subsequently, the data were entered in Microsoft excel spreadsheet, coded and analyzed using SPSS 23. Descriptive analysis was carried out for the socio-demographic factors, frequency of self-medication, indications for practicing self-medication, most common medications used for self-medication, sources of information and influencing factors along with the attitude towards self-medication. We also studied the association between the various parameters mentioned in the sociodemographic profile with the practice of self-medication.
Conclusion: Our study has shown that the practice of self-medication is prevalent to the extent of 81.4% among the non-teaching staff of our college. We found that there were quite a few reasons why people self-medicate. Our finding of association of larger family size with greater prevalence of self –medication is novel.
31. A Retrospective Comparative Assessment of the Changing Profile of Cutaneous Manifestations of HIV after the Advent of Antiretroviral Therapy
Aswini Kumar Das
Abstract
Aim: The primary objective of this study is to evaluate cutaneous manifestations of HIV in patients on antiretroviral therapy, as compared to patients who are not on antiretroviral therapy.
Methods: This was a retrospective study conducted in the department of Skin and VD, Lord Buddha Koshi Medical College and Hospital, Saharsa, Bihar, India.100 records were included in the analysis. These were classified as antiretroviral naïve (50 medical records) and antiretroviral experienced (50 medical records).
Results: Of the 100 patients included in the analysis, 40 (40%) were on antiretroviral therapy while 60 (60%) were antiretroviral naive. 48 patients (48%) were male while 52 (52%) were female. For patients on antiretroviral therapy, the majority (45%) were in the age group 36 to 45 years. The majority of antiretroviral naive patients (36.67%) were in the age group 36 to 45 years.
Conclusion: Early recognition of the cutaneous manifestation can help in better management of HIV infection in resource-poor setting, as it can indicate the progression of the disease and underlying immune status.
32. Prospective Comparative Assessment of Cemented Versus Uncemented Hemiarthroplasty of the Hip for Displaced Neck of Femur Fractures
Balmiki Kumar Das
Abstract
Aim: To compare cemented versus uncemented hemiarthroplasty of the hip for displaced neck of femur fractures.
Methods: The prospective comparative study was conducted in the Department of Orthopaedics, ICARE institute of Medical sciences and Research & Dr.Bidhan Chandra Roy Hospital, Haldia, West Bengal, India included 50 cases of intracapsular fracture neck of femur in the elderly aged more than 60 years where 25 patients were treated by hemiarthroplasty using uncemented fenestrated prosthesis whereas 25 patients were treated with hemiarthroplasty using cemented non-fenestrated prosthesis.
Results: Total 50 patients with fracture neck femur were operated on for hemiarthroplasty, cemented or uncemented, during the study period. The mean age was 66.30 ± 5.78years with the cemented cohort and 64.36 ± 6.20years in the uncemented cohort. Of these, 22 (44%) were men and 28(56%) were female. The most common mechanism of injury was a trivial fall (88%) as opposed to a road traffic accident (12%).
Conclusion: Bipolar hemiarthroplasty whether cemented or uncemented is an excellent treatment for fracture neck femur. No significant difference between both methods in terms of functional outcome. Cemented hemiarthroplasty results in more blood loss and takes more operative time but is associated with less post-operative pain and complication and better functional outcome.
33. Management of Osteoarthritis: Clinical Efficacy of Nutraceuticals
Sanjay Kumar Gupta
Abstract
Aim: The aim of the present study was to evaluate the marketed product TriNyros (combination of Rosehip, IridoForceTM, Aflapin) (Nutragenix Healthcare Pvt. Ltd.) as an additive treatment in OA patients and its effect in patients with & without comorbidity.
Methods: A phase IV post marketing surveillance study of Cap. TriNyros (Nutragenix Healthcare Pvt. Ltd.) was conducted at Department of Orthopaedics, Shree Narayan Medical Institute & Hospital, Saharsa, Bihar, India for 1.5 years. During the study total 80 patients were selected based on inclusion and exclusion criteria in which comprise 30 (37.5%) males and 50 (62.5%) females. The mean age of the subject was 58.60 years, and 70% patients belong to the age group above 50 years. Out of 80 patients, 75% patients had comorbidities such as hypertension, anxiety, diabetes mellitus, thyroid disorders etc. All the subjects selected during the study received TriNyros capsule two times daily for three months.
Results: During analysis of clinical symptoms parameters such as joint line tendinitis on palpations, limitation of mobility, joint crepitus, swelling and redness were included in the study. The treatment with TriNyros for 3 months leads to 60.64% reduction in pain on palpations of OA patient. Movement of a joint affected by OA may cause a crackling or grating sensation called “crepitus”. The reduction rate for joint crepitus is similar in OA patient with comorbidity (72.65%) & without comorbidity (66.70%).
Conclusion: OA as it has an important effect on the treatment. Finally, only one fixed dose of TriNyros was used during the study to evaluate its efficacy; hence we could not validate effect of different doses on safety and efficacy in OA patient. The findings of the current phase IV post marketing surveillance suggest that TriNyros (Nutragenix Healthcare Pvt. Ltd) act synergistically to exert anti-inflammatory/anti-arthritic activity. Cap TriNyros efficaciously reduces joint pain and improves the physical functional ability of OA patient.
34. Assessment of Nasal Bones and Piriform Apertures in Human Skulls: A Morphometric Study
Vishwajeet Kumar
Abstract
Aim: The present study was undertaken to evaluate the dimensions (maximal width and length), the size and the shape of the piriform aperture (PA) and nasal bone.
Methods: 70 adult dry skulls of were collected from the Department of Anatomy of Lord Buddha Koshi Medical College and Hospital, Saharsa, Bihar, India. All measurements were taken using digital Vernier caliper accurate up to 0.001 mm. Nasion and anterior nasal spine was marked. Then nasomaxillary and internasal sutures were traced.
Results: It is evident from Table 1 that height, upper width and lower width of piriform aperture were greater in male as compared to female. This difference was not statistically significant for upper width of piriform aperture (p=0.59) and for lower width of piriform aperture (p= 0.75) while the difference in height of piriform aperture was statistically significant. (p <0.0001).
Conclusion: The width of piriform shows an equal average for both sexes. The results obtained in this study showed the importance of the morphological knowledge of the piriform aperture.
35. A Hospital-Based Observational Evaluation of Serum 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D Levels in Alopecia Areata of Scalp
Aswini Kumar Das
Abstract
Aim: The aim of the study was to evaluate serum 25(OH) D levels in patients with AA and correlate with severity.
Methods: It was a hospital-based cross-sectional observational study conducted in the department of Skin and VD, Lord Buddha Koshi Medical College and Hospital, Saharsa, Bihar, India involving fifty untreated cases of alopecia areata of scalp, between 18-50 years of age, diagnosed clinically by the presence of well defined, round/oval, smooth bald areas of non-scarring hair loss with presence of exclamation mark hair for one year.
Results: A total of 50 cases and 50 controls satisfying the inclusion and exclusion criteria were included in the study. Baseline clinical characteristics of cases and controls have been illustrated in (Table 2). The majority of cases of AA included in the study (45%) were between 21-30 years of age and least number of cases (5%) were recorded in age group of >40 years. The mean age noted in the present study was 25.07±7.40 years.
Conclusion: The trend toward the increased percentage of vitamin D-deficient individuals among AA patients seen in this study may provide insight into the association of vitamin D with AA. The factors that can help determine which AA patients will benefit from vitamin D testing in an AA setting include high SALT scores, younger age, female sex, sun exposure of \30 minutes per day, and lighter skin photo type.
36. A Prospective Assessment of the Functional Outcome of Arthroscopic Suture Pull out Fixation of Displaced Tibial Spine Avulsion Fracture
Balmiki Kumar Das
Abstract
Aim: The present study was conducted to assess the functional outcome of arthroscopic suture pull out fixation of displaced tibial spine avulsion fracture.
Methods: The present prospective study was conducted in the Department of Orthopaedics, ICARE institute of Medical sciences and Research & Dr. Bidhan Chandra Roy Hospital, Haldia, West Bengal, India over a period of 1 year with a sample size of 50.
Results: Total 50 patients with tibial spine avulsion were operated on with arthroscopic pull out suture technique. The majority of subjects were in the age group 18 to 30 years (60%).In the study, 80% were males and 20% were females.
Conclusion: The present study concluded that Arthroscopic suture pull-out fixation for type III and IV tibial spine avulsion shows excellent outcomes without any significant complications.
37. Assessment of the Risks of Not Regaining to the Pre-Fracture Mobility Level after Hip Fracture Surgery in Elderly Patients
Sanjay Kumar Gupta
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the functional recovery at six months postoperatively in elderly patients with hip fractures and to determine the risks of not regaining to the pre-fracture mobility level.
Methods: The present study was conducted in the Department of Orthopaedics, Shree Narayan Medical institute and Hospital, Saharsa, Bihar, India, which the ethics committee approved, 430 consecutive patients over the age of 65 who were admitted to the hospital with hip fractures for 2 years were examined.
Results: 120 (60%) of the patients were female and 80 (340%) were male, with a mean age of 78.8±9.4 years. There were 150 (75%) intertrochanteric fractures and 50 (25%) femoral neck fractures. 100 (50%) patients underwent proximal femoral nail (PFN), 80 (40%) patients underwent hemiarthroplasty, 12 (6%) patients underwent dynamic hip screw (DHS) and 8 (4%) patients underwent total hip arthroplasty. In the analysis performed to determine the level of mobility, it was found that 160 (80%) patients moved without the use of an aid and 40 (20%) patients moved with the use of an aid in the pre-fracture period.
Conclusion: Advanced age, high ASA score, cardiovascular disease or malignancy among comorbidities, intertrochanteric fracture as fracture type, and use of PFN as implant type were the main risk factors for not regaining to pre-fracture mobility and ADL.
38. Assessment of Branching Pattern of the Axillary Artery: A Cadaveric Study
Vishwajeet Kumar
Abstract
Aim: The aim of the present study was to contribute to the existing knowledge of the variations in the branching pattern of the Axillary artery, explaining its embryological basis and also its morphological and clinical significance.
Methods: 20 cadavers (40 upper limbs) – 15 male and 5 female embalmed with 10% formalin were dissected for this study. The study was conducted at Department of Anatomy, Lord Buddha Koshi Medical College and Hospital, Saharsa, Bihar, India. Variations in the origin and branching pattern of axillary artery were noted.
Results: Variable branching pattern was observed in 7% of the cases on right side and 8% of the cases on left side in first part of Axillary artery, 43% of the cases on right side and 52% of the cases on left side in second part and 50% of the cases on right side and 25% of the cases on left side in third part.
Conclusion: Accurate and detailed knowledge of the normal and variant anatomy of the axillary artery is of importance for anatomists, surgeons, radiologists and clinicians during various interventional, diagnostic, therapeutic and surgical procedures on pectoral and axillary regions.
39. A Comparative Study on the Impact of Side effects of Antihypertensive Drug Classes on Adherence to Medication
Glory Josephine I., Sriram S.
Abstract
Background: Hypertension is the most common chronic illness and one of the most important risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Medication nonadherence is the leading cause of uncontrolled hypertension, which has become a significant concern in developed countries. The side effects of first -line drugs such as Diuretics, Calcium channel blockers and Angiotensin receptor blockers could be accounted for the non-adherence.
Aim and Objectives: The study was focused on determining the impact of the of first-line antihypertensive class side effects on drug adherence.
Materials and Methods: The study compared the adverse effects of Diuretics, Calcium channel blockers and Angiotensin receptor blockers using structured questionnaires. The side effects, severity and adherence were calculated by assessing the Physical symptom distress index (PSD), Overall symptom distress index (OSD) and pill count adherence ratio (PCAR).
Results: In total 39.3% (22 out of 56 patients) at the end of 4 weeks and 41.1% (23 out of 56 patients) at the end of 8 weeks experienced side effects. Diuretics had a higher mean OSD (3.56) than the Calcium channel blocker (1.75) and Angiotensin receptor blocker (0.60). Angiotensin receptor blocker produced side effects in 25% of people consuming it and medication adherence of 70%. Following that, the Calcium channel blocker produced side effects in 45% and medication adherence in 60% of the patients. However, Diuretics have side effects of 56.3% and medication adherence of 62.5%.
Conclusion: The above study proved that Angiotensin receptor blockers produced fewer side effects and more drug adherence than CCB and diuretics. This suggested that side effects might substantially affect antihypertensive drug adherence.
40. Impact of the Second Wave of COVID 19 on Maternal and Fetal Outcome in Tertiary Care Centre and its Comparison with the First Wave – Observational Study
Rekha Wadhwani, Juhi Agarwal, Poorva Badkur, Padma Bhatia
Abstract
Introduction: The emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, have similar effect on pregnant women as influenza or other coronavirus infections. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic is likely to be context specific and differ depending on a variety of country-specific factors. A global pandemic is likely to only reveal its consequences after significant time passes, and literature published before or immediately after policies are implemented may not capture all relevant outcomes.
Material and Methods: The study was conducted in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Gandhi Medical College, Bhopal. It included all antenatal COVID 19 patients which reported to the hospital during April 2020 to May 2021, 1st wave from April 2020 to December 2020 and second wave from Jan 2021 to May 2021 after taking due informed consent. The detailed history and full clinical and general examination were performed using a predesigned proforma. The antenatal patients were categorized into mild, moderate and severe COVID. Data on clinical manifestations, laboratory tests, maternal and perinatal outcomes were extracted and analysed. The comparisons of 1st wave and second wave was done.
Results: There were 210 confirmed pregnant women with coronavirus disease (COVID-19). 26 maternal deaths occurred from these confirmed cases. Compared to pregnant women without COVID-19, pregnant women with a confirmed COVID-19 diagnosis had an increased risk of maternal complications and caesarean section. In initial months (April 20 to December 20) there were 89 confirmed cases of covid 19 and 4 maternal mortality and from January 21 to May 21 there were 121 cases and 22 maternal deaths. The second wave has taken greater toll on life of pregnant women.
Conclusion: In the second wave, pregnant women with severe or critical coronavirus disease were admitted to the ICU, intubated if they require mechanical ventilation, and were at increased risk of composite morbidity. Thus, the second wave affected the pregnant women in a much serious way and the maternal as well as fetal outcome were very poor.
41. A Prospective Randomized Comparative Study between Combined Sciatic- Femoral Nerve Block and Spinal Anaesthetic Block for Unilateral below Knee Surgery of Lower Limb
Pal S, Srivastava L, Majumdar S, Chakraborty S, Sarkar M, Rudra J
Abstract
Introduction: Aim was to study the combined sciatic-femoral nerve block in operative management for unilateral below knee surgery and to compare the hemodynamic parameters in these nerve blocks with commonly used subarachnoid block.
Material and Methods: 70 patients of 20 to 60 yrs, ASA grade I and II, had undergone unilateral below knee surgery of lower limb were divided into two groups – the spinal anaesthetic block group (SAB) and the sciatic femoral nerve block group (SFB). In SFB group femoral block was performed by paravascular approach (three-in-one block) and sciatic nerve block was given by classic Labat approach. Patients in SAB group were received subarachnoid block using 25 G Quincke’s needle in L3-4 interspace with 3.5 cc hyperbaric inj. Bupivacaine (0.5%). Post-operative pain was measured by Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) score at every 4 hours interval for 36 hours.
Results: The mean sensory and motor block onset time and duration in SFB group was much higher than SAB group. The post-operative pain by VAS score was found statistically significant from 8 to 28 hours (p < 0.05) with higher VAS score in SAB group than SFB group.
Conclusion: Though time consuming, combined Sciatic- Femoral nerve block resulted in better intra-operative haemodynamic control and post-operative pain management than subarachnoid block for unilateral below knee surgery.
42. Impact of Covid-19 Pandemic on Teaching and Training of Orthopaedic Resident in Medical College
Manish Rajpoot, Saurabh Sharma, Akhil Bansal, Ankit Prasad, Gopala Rao Mundlapati
Abstract
Background: Many elective surgeries are getting postponed which directly affect the learning of surgical skill in resident. Various teaching activity such as OPD and bed side teaching also reduced because of decrease load and social distancing. Purpose of the study is to analyse the impact of this pandemic on orthopaedic education of resident in medical college.
Material and Methods: A questionnaire was prepared on Google form for online survey. Total 74 residents responded, in which JR-1 (26), JR2 (24), JR-3 (19) and SR (5) participated. This study is an observational study in which we analysed the impact of this pandemic on orthopaedic teaching and training of resident in medical college.
Result: In this pandemic clinical work in the form of OPD, IPD, no. of surgery (both elective and emergency) observed, assisted, independently performed significantly reduced. This directly affected the skill development of growing orthopaedic surgeon. Classroom teaching and bed side teaching were grossly affected. Some online platforms were used to teach the resident, but they are not as effective as conventional methods. Because of decrease clinical workload resident’s thesis and research work also affected which is an essential part of resident education.
Conclusion: In summary, the results of this online survey on residents showed that there significant impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on teaching and training of orthopaedic resident in government medical colleges of central India.
43. A Retrospective Study of Changing Trends in Maternal Mortality in Tertiary Care Hospital
Nisha Mandloi, Nandini Singh Bhati, Sunil Bajoliya, Shailja Garg
Abstract
Objective: The study intends to review maternal deaths in our institute to study the epidemeology of maternal death and differentiate between treatable and untreatable causes, thus alleviating burden of unfortunate maternal death.
Methods: All maternal deaths due to pregnancy or causes related or aggravated by pregnancy or its management during pregnancy or within 42 days of delivery irrespective of duration and site of pregnancy were included .The maternal mortality forms which were filled by the treating doctor under guidance of senior faculty were scrutinized and cause of death was derived. All the parameters were analyzed using descriptive statistics (percentages and proportions) were calculated.
Results: Among 40 maternal deaths 18 (45.0 %). It was observed that 30 (75.0%) maternal deaths were reported in rural patients. There were 28 (70.0%) deaths among illiterate patients. 28 (70.0%) maternal deaths in patients belonging to below poverty line. Majority 19 (47.5%) were third gravida and more. It was noted that there were 25 (62.5%) deaths of referred patients .15 (37.5%) died in antepartum period and 25 (63.5%) died in postpartum period. 31 (77.5%) died in less than 24 hours and 9 (22.5%) patients died after 24 hours.
Conclusion: Most of the causes of death were treatable. The Anganwadi workers, Accredited social health activist (ASHA) and Auxillary nurse midwife (ANM) are the connecting link between patients living in remote areas and doctors, therefore conducting training programmes for them can bring a major change. We need a holistic approach involving volunteers from various fields to ensure basic healt care facilities equally to every women.
44. Poisoning by Wild Yam: Dioscorea – A Case Report
Saagar Singh
Abstract
People from rural areas, who are less accessible to or are reluctant about medical services, sometimes prefer local traditional medicine practitioner for treatment of common ailments. But because they are not aware of the fact that such practitioners lack scientific knowledge, they suffer the serious consequences of such primitive treatments. These people are often served some kind of a plant root preparation and may lead to a fatal event from an overdose of such medication. One such case is reported here who after the advice of such a traditional medicine practitioner ended in a fatal event as a result of overdose of a root preparation from bitter yam. This article also describes the clinico- pathological aspects of bitter yam poisoning.
45. Prevalence of Polycystic Ovary in Females with Infertility
Alka Jaiswal, Ashvini Bhatnagar, Utsav Singh
Abstract
Introduction: Polycystic ovary (PCO) features have become prevalent in the population due to increasing lifestyle and other genetical factors. There is a significant effect of polycystic ovaries and several consequences have been quite prevalent. It is said that around 10% of females in the reproductive age group have been suffering from Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). One of the notable consequences of PCO features is infertility and there has been much discussion about the high prevalence of PCO features among infertility patients.
Aims and Objective: To find out the prevalence and significance of PCO features among the various infertility patient and also compared them to the patient without infertility.
Methods: This study is of retrospective design which has taken 88 patients with infertility and 32 healthy females of similar age groups, who had a history of successful pregnancy and labour. The baseline characteristics, hormonal profile, and pelvic ultrasound were all performed and they were classified into 3 groups based on their diagnosis or etiological factor of infertility. The control group also underwent all the laboratory tests, hormonal profiling and pelvic ultrasound. The analysis was performed between the groups and within each group among the patients of each group with polycystic features and without polycystic features.
Results: The study has shown that there is a significant difference between the number of patients in the PCO subgroup and the Normal subgroup of each group (p<0.05), the number of PCO subgroup of each group with that of the PCO subgroup of the control group (p<0.05) and PCO subgroup of each group and PCO subgroup of the control group (p<0.05).
Conclusion: The study has concluded that there is a significant number of patients with infertility who have Polycystic features as compared to the number of females with Polycystic features without infertility.
46. Immunomodulatory Effect of Dawa-Ul-Kurkum a Unani Preparation and its Possible Mechanisms in Experimental Model of Ethanol Induced Liver Damage in Rats
Mohd Rafi Reshi, Kavita Gulati, Saman Anees, Maaz Naqvi, Nafaa Hasan, Arunabha Ray
Abstract
Objective: The effects of Dawa-ul-Kurkum a polyherbal Unani formulation was evaluated on ethanol induced hepatotoxicity in rats and its possible causes were investigated.
Methods: Immunoglobulin and cytokine levels were assessed by ELISA kit manual method. Delayed type hypersensitivity reaction by Institoris
et al method.
Results: In the vehicle treated experimental group, ethanol induced significant hydropic degeneration in the hepatocytes as evidenced by increased level of cytokine as well as immunoglobulin, alterations in liver weight and changes in body weight from controls. Dawa-ul-Kurkum (DK), at two different doses, demonstrated strong immunomodulatory and protective effects against ethanol-induced liver damage. DK as well as hydro-alcoholic extarct has immunomodulatory effects comparable to those brought on by silymarin treatment.
Conclusion: It concludes that ethanol-induced hepatotoxicity can be treated with Dawa-ul-Kurkum for immunomodulatory benefits, and it suggests that the polyherbal’s attenuation may be the mechanism of action for such effects.
47. Clinical Spectrum of Psoriatic ArthropathySeen in Patients Attending Tertiary Care Hospital
Suhasini Arra, S. Vasantha Kumari, Sirish Kumar Shenkeshi, Bliss D Agape
Abstract
Background: Psoriatic arthritis is a chronic disease with exacerbations and remissions for which a complete, permanent cure has not been found. In this study, an attempt is made to characterize the different types of joint involvement in psoriatic arthritis, detect the precipitating factors, and correlate the radiological features.
Methods: This study was conducted in the Departments of Orthopedics/Dermatology, Kakatiya Medical College, and MGM Hospital, Warangal. Detailed history and a complete musculoskeletal and cutaneous examination were done for these selected patients and findings were recorded on a pre=designed proforma. Rheumatoid factor was done in all patients and only those who were RA factor negative were included in this study. All patients in the study were subjected to the radiological examination of joints. Radiographs were done only for joints with evidence of arthritis, in the form of tenderness, swelling, or loss of mobility.
Results: Average age of patients examined was 43.2 years, males 42.9 years, and of females 43.8 years. The male to female ratio was 2.8:1. Onset of skin involvement was at an average of 35.1 years whereas that of the joint was 39.3 years. The average age of onset of skin involvement in males was 34.7 years and in females was 36.3 years. The average age of onset of joint involvement in males was 39.2 years and in females was 39.6 years There was a definite male preponderance in the patients with psoriatic arthropathy. This is true of all the subtypes, except in the arthritis mutilans subgroup. The male preponderance was most prominent in the oligoarticular group.
Conclusion: Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) has a male predilection and they had an earlier onset of oligoarticular and axial involvement. The small joints of the right hand are more involved than the left and housewives had more symmetric RA like and DIP type of PsA. Many patients with psoriatic spondyloarthropathy followed a sedentary lifestyle with respect to occupation. In patients with a shorter duration of arthropathy, radiographs were either normal or showed soft tissue swelling alone, with the absence of bony changes.
48. Spectrum of Lesions on Upper GI Endoscopy at a Tertiary Care Centre of Central India
Sagar Anand, Sagar Unique, Chaturvedi Neha
Abstract
Background: The diversity of the symptoms of upper gastro intestinal tract disorders bring a lot of patients for evaluation by upper gastrointestinal endoscopy wherever available. Upper gastrointestinal diagnostic evaluation helps to distinguish and determine the diagnosis ranging from functional disorders to carcinoma. Endoscopy has greatly facilitated in diagnosis of the ailments of the upper GI tract.
Aims: To study the spectrum of lesions diagnosed on upper gi endoscopy at a tertiary care centre.
Setting & Design: It is an observational study. Patients who reported to endoscopy unit for upper gi endoscopy from various departments were subjected to endoscopy.
Material and Method: 200 upper gastro-intestinal endoscopies were performed after a meticulous history and examination. The various diagnosis observed were taken into consideration with proper statistical analysis was done.
Results and Conclusion: In our study we observed 58(29%) patients with oesophageal varices, followed by 42 (21%) patients diagnosed as gastritis, 15(7.5%) patients with oesophagitis, 4 (2%) patients with gastric ulcer, 1(0.5%) patient with duodenal ulcer, 7 (3.5%) patients with abnormal growth and 32 (16%) patients with miscellaneous diagnosis including infective lesions, hiatal hernia and others.
49. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects of Withania Somnifera In. an Experimental Model of Bronchial Asthma in Normal and Stressed Rats
Maaz Naqvi, Sana Rehman, Nafaa Hasan Ali, Kavita Gulati, Arunabha Ray
Abstract
Introduction: Airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness are distinctive features of bronchial asthma and chronic inflammation may lead to structural changes known as airway remodelling. Complex and interacting mechanisms regulate the pathophysiology of asthma and confounding factors like emotional stress have been implicated.
Withania somnifera (WS) is a potent anti-stress and immunomodulator in view of which it could be considered as possible therapeutic agent for asthma.
Objective: The present study examined the anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of s WS root extract on markers of airway inflammation and immunity in normal as well as stressed rats in experimentally induced bronchial asthma.
Methods: Wistar rats (200-225 g) were immunized with ovalbumin (OVA) + aluminium hydroxide on day 1 and challenged with OVA on day 14. The rats were divided into stressed (RS x 15 days) and non-stressed groups and were administered WS extract (200 and 400 mg/kg). Following this, the animals were sacrificed, and Broncho alveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and blood were collected for assay of immune and inflammatory markers of the airways.
Results: WS extract significantly decreased OVA-induced elevations in IgE, IL-4, TNF-α and IL-13 levels in both blood and BALF in RS exposed and non-RS rats with the higher dose of WS. These WS effects were comparable to those seen after dexamethasone treatment. Further, the OVA-induced responses in RS-exposed rats and their modulation by WS were of greater magnitude as compared to their non-RS groups.
Conclusion: Our study findings indicate that WS extract effectively attenuated markers of immunity and airway inflammation in stressed and non-stressed rats, in the OVA model of asthma and suggests that anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory and anti-stress effects could contribute to these responses.
50. Sciatic Selective Motor Fasciculotomy and Hamstring Lengthening for Spastic Knee Flexon in Cerebral Palsy in Tertiary Care Hospital, Telangana State
E. Rajendra Kumar, Venkateshwara Prasanna Govindappagari, A.K. Purohit
Abstract
Aim: To develop a surgical technique for relieving harmful hamstring spasticity without much deterioration in muscle power and help to improve preexisting motor functions, provide comfort and relief pain.
Material & Methods: A total of 30 patients underwent Sciatic SMF in the Tertiary Care Hospital, Telangana State. Twenty out of these 30 patients who had at least six months follow-up were included in this study.
Results: There were 30 patients who underwent sciatic and 20 patients could be followed-up. These 20 patients have been evaluated. There were 8 patients who underwent only SMF and did not require STR, while there were 12 patients who required both SMF and STR.
Conclusion: Sciatic SMF help in improving motor functions. The improvement is seen in existing motor function in most of the cases. However, maximum improvement is seen in case having good control in lower limbs.
51.
To Study Correlation of Oxidative Parameters and CD4 Count in HIV Patients Before and After 3 Month of HAART
Vaibhav Singh Chauhan, Arpit Verma, Supriya Sharma, Kale BP
Abstract
Background & Method: The aim of this study is to study correlation of oxidative parameters and CD4 count in HIV patients before and after 3 months of HAART. Hematological profile and CD4 count were collected from routine investigations done during the visit in HIV OPD for 200 participants, before beginning of treatment and following after 3 months of starting HAART. Oxidative parameters like Total antioxidant capacity (TAC), nitric oxide (NO) and vitamin E were done in first 100 participants from the above 200 participants, before beginning treatment and following after 3 months of starting HAART.
Result: there was significant improvement in Total Antioxidant count and vitamin E levels with CD4 levels(CD4 ≤350 and CD4>350).Also the haematological parameters like haemoglobin,WBC count improved after 3 months of HAART.
Conclusion: HAART is indispensable as these individuals are in danger and risk of progression of disease and death. In this manner screening for clinically important hematological parameters preceding to initiation of HAART and also during HAART must be prioritized. Also other factors should be considered as gender based risk, nutritional status and other contributing components responsible for immune suppression. Highly significant correlation is seen with hemoglobin and CD4 count, as Hb increases there is also increase in CD4 count. Along these lines of screening of hematological parameters before and during treatment is very important so as to intervene where the abnormalities would be potentially reversed. Randomized controlled trials on a big population taking HAART is necessary to affirm the causal pathway between HIV burden, hematological variations and clinical outcome.
52.
Insomnia and Related Anxiety among Medical Students
Varsha Davis, Rajveer Singh Nirwan, Brajesh Kumar Pushp, Rajendrakumar Katte
Abstract
Objective: Objective of this study is to determine the prevelance of insomnia in medical students and also to identify anxiety related insomnia.
Method: This is a cross sectional study to determine prevalence of insomnia in medical students with sample size of 190 students. Questionnaire consisted of socio-demographic characteristics along with questions related to insomnia for anxiety.
Result: Students with sub-threshold, moderate and severe insomnia were 48.9%, 17.4%, 3.7% respectively. 50% students who were insomniacs had mild anxiety.
Conclusion: Study concludes that prevalence of insomnia in medical students are high. There is significant association between insomnia and anxiety.
53.
Evaluation of Spectrum of Dermatological Morbidity Pattern at Tertiary Care Hospital: A Retrospective Study
Chandra Prakash Purohit, Harish Chandra Sanadhya, Shivani Bhardwaj
Abstract
Background: Skin diseases have gained a lot of interest over the past decades because they are potentially preventable, controllable and prevalent worldwide. In 2019, skin diseases reported as the fourth leading disease among non-fatal disease burden globally and also accounts for 18th leading cause of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) worldwide.
Material & Methods: The present retrospective study was conducted at department of general medicine of our tertiary care hospital. Institutional Ethics Committee Clearance was obtained before start of study and written and informed consent for the procedure was obtained from all the patients. Strict confidentiality was maintained with patient identity and data and not revealed, at any point of time.
Results: The most common presentation was skin infections present among 416 (23.66%) patients. After skin infections the next common finding was eczema which was present among 256 (16%) patients which was followed by contact dermatitis among 192 (12%) patients, which was followed by urticaria found in 168 (10.5%) patients and which was followed by xerosis present in 144 (9%) patients which followed by acne found in 128 (8%). Hair disorders was present in 120 (7.5%) cases which was followed by atopic dermatitis present in 96 (6%) cases. Post inflammatory changes were seen in 64 (4%), vitiligo was present in 32 (2%) cases followed by P.alba in 24 (1.5%) cases which was followed by psoriasis found in 16 (1%) patients. Oral lesions, nutritional disorders and pemphigus vulgaris were present in 16 (1%) patients respectively, keratosis pilaris and melasma was present in 8 (0.5%) patients, keloid was found in 4 (0.25%) patients and hypertrophic scar was present in 2 (0.125%) cases.
Conclusion: We concluded from the present study that the most common presentation was skin infections present among study patients. Fungal diseases were the most common infection and eczema and contact dermatitis were seen more commonly and scabies was the most common infestation. The climate, occupation, socio-economic status, gender and age of the patient were associated in the occurrence of skin diseases.
54.
Fetal Dissection of Human Lungs Morphological Analysis
Bhuwnesh Kumar Sharma, Surendra Kumar Sharma
Abstract
Background: The vital components of breathing are the lungs. They take up the majority of the thoracic cavity and are located on either side of the heart and other mediastinal structures. Except for where it is linked to the mediastinum at the hilum and pulmonary ligament, each lung is free within its pleural cavity. A fresh normal lung that has been removed from the thorax is spongy, may float in water, and crepitates when handled due to the air in its alveoli. Additionally, it is quite elastic, thus when taken out of the thorax, it retracts. The locations of contact between its most periphery lobules and the pleural surface are indicated by thin, black lines that cut through its smooth, shining surface to form numerous small polyhedral domains. As a result, the current study offers extensive information about the morphological features of typical fetal and fetal lung development as well as the histogenesis of the fetal lung in the general population. In relation to body size, men’s lungs are heavier than women’s, while boys’ lungs are larger than those of females. Air volume, pulmonary tissue volume, and lung volume all rise linearly with body length. A rare fetal anomaly known as pulmonary agenesis, which is linked to congenital heart disease, causes the absence of pulmonary arteries, bronchi, and lung parenchyma.
Aim: Fetal dissection of human lungs morphological analysis. To establish standard reference morphometric data for developing human fetus as well as fetal lungs. Gaining a more substantive insight into the normal events and characteristics of human prenatal development.
Material And Method: This study was carried out in the Department of Surgery of Civil Hospital with the proper approval of the ethics committee, the medical director, and the department head. The abortus/fetus used in this study were gathered from the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 40 fetuses between the ages of 14 and 40 weeks were gathered. For the benefit of the parents and close relatives, the consent form was written in both Hindi and English. Once we receive information from sister-in-charge of labor room about availability of fetus, we immediately rushed to the labor room.
Results: the mean fetal weight and means of weight of right and left lungs as per the group distribution. It was observed from the data that the rate of increase in weight of the lungs were similar to the increase in the body weight for the initial weeks of development. But during the last weeks of gestation i.e., 33 – 40 weeks, the increase in weight of lungs slows down as compared to the fetal weight increase. It is observed that increase in the width of both of the lungs is suddenly increased during the gestational age of 33 – 40 weeks. The width of both of the lungs is almost double for the group for as compared to group 3. Similar pattern was also observed in other parameters like thickness as well as circumference of right and left lungs.
Conclusion: It was concluded that in the present study that fetal weight in the population is lower than the same from Nepal as well as Eastern India. Up to second trimester end, the Gujarati fetuses were found to be heavier than the American fetuses. At terms, the Dennis, the Australian and the Gujarati fetuses were comparable in weight. In the last trimester, fetuses of Gujarati population weigh lighter than the same from the French.
55.
Fungal Disease of the Nose and Paranasal Sinuses
Prithvi Raj Singh, Krishna Murari Bansal
Abstract
Background: Because fungi are so common in nature, it is impossible to avoid coming into contact with the Sino nasal and respiratory epithelium. The spectrum of the disease varies from noninvasive disease to acute and fulminant infection, each with specific clinical and histopathologic symptoms (Table I). Inhalation of these organisms can induce both acute and chronic rhinosinusitis. In the care of patients with invasive fungal rhinosinusitis, topical or systemic antifungal therapy can play a key role and should be combined with surgical intervention. However, these treatments have a limited impact in the treatment of noninvasive infections. Only dermatophytes are transmissible from host to host among the majority of fungal species that are harmful to humans and cause opportunistic illnesses. It has been severely understated how often fungus cause illnesses and deaths.
Aim: to research the prevalence of nasopharyngeal and paranasal sinus fungus in our area. to research the pathological and clinical effects of nasopharyngeal and paranasal sinus fungus.
Material and Method: Patients who visited the ENT outpatient department provided the materials for the current investigation. A total of 50 patients were evaluated using a standard proforma and completed the following investigative techniques systematically as and when necessary in order to rule out fungal infections of the nose and paranasal sinuses. As part of the initial investigations, complete hemograms, blood sugar levels, serum electrolytes, serum proteins, blood grouping, etc., were performed to examine the patient’s overall health state and rule out any underlying illnesses. All patients had the necessary X-rays of their noses and paranasal sinuses taken, and those who had fungal granulomas were also given contrast-enhanced CT scans of their noses, paranasal sinuses, and brains.
Results: There were 50 individuals studied, and of those, 18 were men and 32 were women. They were all of Indian descent. In this survey, there were more women than men. In this study, females made up 64% of all the cases. Nasal symptoms were present in 100% of the individuals in our research. They are post-nasal discharge and nasal discharge blockage. frequent sneezing, nasal hemorrhage, and a diminished or absent sense of smell (Hyposmia or Anosmia). In our study, 16% of participants had ocular symptoms like proptosis, epiphora, and diplopia, which cause vision impairment. According to our study, out of 50 patients, 22 had Aspergillus flavus, 6 had Aspergillus fumigatus, 3 had Aspergillus niger, and 2 had Aspergillus terreus. Histopathology revealed that all cases were Aspergillus fungal cultures.
Conclusion: The term “fungal rhinosinusitis” refers to a variety of fungal diseases, from asymptomatic colonization of the sinus cavities to infections that advance quickly and are eventually lethal. The long-term prognosis for patients with invasive fungal rhinosinusitis is poor, necessitating debridement in up to 43% of cases due to extensive morbidity from extension to the palate, maxilla, orbit, and cranium. However, more recent data suggest that rapid multidisciplinary treatment may have significantly reduced morbidity.
56.
Assessment of Platelet Indices and Counts and Their Impact in Pre- and During Eclampsia
Yogesh Chandra Sharma, Shalini Sharma
Abstract
Background: Three to eight percent of pregnancies are complicated by preeclampsia, one of the primary health issues that contribute to maternal morbidity and mortality. Preeclampsia’s pathophysiology has been theorized to be influenced by changes in coagulation and fibrinolysis. The most serious health danger to both the mother and the fetus during pregnancy is preeclampsia. The use of platelet characteristics in preeclampsia diagnosis is not expanding in Ethiopia, despite the fact that they are one of the proposed indicators for the prediction of preeclampsia. Preeclampsia and normal pregnancy’s platelet patterns are not well understood.
Aim: The purpose of this study is to determine how platelet counts and indices relate to pre-eclampsia and eclampsia. The goal of this study was to identify the platelet index pattern in preeclamptic women in our study population.
Material and Method: The study was conducted in the Department of Pathology and was prospective with case control. The study included 100 consenting patients, 50 cases of pre-eclampsia (blood pressure> 140/90 mmHg and proteinuria > 300 mg/day in patients > 20 weeks gestation) and 50 healthy pregnant women of similar age with a gestational age of at least 20 weeks. Prior to enrollment, participants received written informed consent with information on the study objectives, impact and significance of the data from. All information was anonymized to protect confidentiality. The control group for the study consisted of 100 healthy pregnant women with no diagnosis of preeclampsia, gestational or chronic hypertension, or proteinuria, with identical demographics and gestational age. An automated hematology analyzer was used to test the blood samples.
Results: In the current study, the average age of the pregnant women was 14.37 + 2.36 years. When compared to the control group, the platelet count in the pre-eclampsia and eclampsia groups had dramatically dropped. Comparing the pre-eclampsia patients to the control group, the MPV, PDW, and P-lcr levels were all elevated according to the degree of pre-eclampsia. While the fundamental characteristics (age, parity, and BMI) of the two trial groups (50 women in each arm) did not statistically differ, the gestational age was significantly lower in the preeclampsia patients.
Conclusion: The estimation of platelet indices approach can be thought of as an early, affordable, and quick procedure for determining the severity of PIH cases, to sum up. Platelet indices can be a helpful screening test for the early detection of pre-eclampsia and eclampsia in the clinical setting. Additionally, platelet indices can determine how pregnant women will fare with this illness. In both pre-eclampsia and eclampsia, platelet status can be regularly determined with P-lcr. Thus, maternal and perinatal outcomes may be significantly impacted by platelet indices. Preeclampsia was linked to an increase in MPV and PDW.
57.
To Study the Clinical Features and Laboratory Profile of Children with Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Vikas Saxena, Ricky Mittal
Abstract
Background: Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) includes a group of disorders that result from reduced activity of several enzymes which are required for the synthesis of cortisol in the adrenal cortex. The prevalence of CAH varies according to the ethnicity and geographic area. Deficiency of 21- hydroxylase enzyme accounts for more than 90% of the cases of congenital adrenal hyperplasia with an incidence of 1 in every 15,000 to 20,000 births.23 Nearly 70% of the affected children due to21 hydroxylase deficiency present with salt wasting form and 30% present with simple virilising form. Prenatal diagnosis and treatment is offered to families who have an affected child with CAH and it has the advantage to prevent ambiguous genitalia in female fetus due to virilization.
Aim: To examine the clinical characteristics and test results of children with congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
Material and Method: Every child with CAH got a thorough clinical examination and full history. They had their anthropometry, sexual maturity rating (SMR), and blood pressure measured. For the purpose of comparing bone mineral values, 20 kids with congenital adrenal hyperplasia and 20 healthy age- and sex-matched controls were used as the sample size. Children with CAH had their serum levels of sodium, potassium, ionized calcium, and alkaline phosphatase measured using a Roche automated electrolyte analyzer. Hyponatremia was defined as serum sodium less than 135 mmol/L and hyperkalemia was defined as serum potassium more than 5.5 mmol/L. The normal serum ionized calcium level is 1.1-1.3 mmol/L and the alkaline phosphatase level is 72-307 IU/L. 17 hydroxy progesterone was measured by solid phase enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)-DRG.
Results: There were a total of 20 children with congenital adrenal hyperplasia during the recruitment period (CAH). Five of the 20 children had the typical salt-wasting CAH, two had the straightforward virilizing CAH, and three had the non-classical CAH. Only 10 children with classical salt wasting CAH were enlisted for the study’s purposes as the study group. Ten healthy youngsters who were age- and sex-matched were recruited as the controls.
Conclusion: The potential for prenatal and even preconception CAH diagnosis is provided by developing technologies. With growing knowledge of the potential effects of prenatal androgen exposure, ongoing conversations regarding the gender of raising for very virilized females are necessary, even though early diagnosis may be useful for counseling parents. Additionally, more research on this population’s sexuality and quality of life indicators is necessary. Most importantly, cutting-edge therapy approaches like modified release hydrocortisone preparation may improve patients with CAH’s quality of life.
58.
Bacterio-etiologic Profile in Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: An Observational Study
Girijesh Kumar
Abstract
Aim: The study was carried out to find out the bacterial etiology in the course of disease and their drug sensitivity pattern.
Methods: All hospitalized patients diagnosed with AECOPD admitted in the hospital were evaluated . The individual bacterial isolates and their sensitive pattern to various antibiotics were also recorded in all one hundred 200 patients. The study was carried out COPD was diagnosed according to the Global Initiative for Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) guidelines.
Results: Out of 200 patients, clinically diagnosed as AECOPD, 80% were males and 20% were females. 40% patients were in the age group 56-65 years followed by 66-75 (25%) age group. Out of a total 200 cases, 80 (40%) were positive for pathogenic bacteria and 120 (60%) were non-pathogenic. Among total 45 pathogenic microbial, 64% were Gram-negative bacteria and 36% were Gram-positive bacteria. Out of 100 pathogenic bacteria, K. pneumoniae was the commonest (36%) followed by P. aeruginosa (23%), S. aureus (16%), S. pneumoniae (12%), S. pyogenes (5%). Among antibiotics, Amikacin was found highest sensitive followed by Azithromycin (67%), Amoxy Clavulanic acid (65%), Ciprofloxacin (60%) and Gentamycin (54%). However, Levofloxacin and Co-trimoxazole were found to be highly resistant 66% and 60% respectively among the drugs used in culture and sensitivity of 100 isolated pathogenic bacteria.
Conclusion: Repeated exacerbation and hospital admission leads to a major impact on the quality of life of patients with COPD. Antibiogram helps in screening resistant pathogens and prescribing right treatment protocol.
59.
Assessing Efficacy of Modified Triple Assessment in the Diagnosis of Breast Lump: An Observational Study
Barun Kumar
Abstract
Aim: The aim of the present study was to assess sensitivity and specificity of modified triple assessment in diagnosis of breast lump.
Methods: The present study was conducted in the Department of General Surgery, Lord Buddha Koshi Medical College and Hospital, Saharsa, Bihar, India for the period of 2 years and randomly selected 200 female patients with breast lump attending surgery OPD and admitted in female surgical ward surgical unit during the study period.
Results: Mean age was 34.56 ± 12.80 years. Youngest patient was of 16 years of age and oldest patient was 70 years of age. In present study the breast lump was present more on right side 110 patients as compared to left side 90. As from present study we can observed that most common size of lump was in range of >2 cm to 5 cm in diameter in clinical breast examination are 130 patients and in 90 patients, size of lump is more than 5 cm in diameter. Most of the patients who went under clinical breast examination yield that mostly the patients with lump in firm consistency 128 patients, 2 of them had soft and other 70 patients had hard in consistency. 80% patients had well circumscribed mass with regular margins followed by Density lesion with microcalcification, irregular margins and speculation (10%). In the study, 44% patients had Fibroadenoma, 20% patients had Ductal cell carcinoma and 16% patients had Fibro adenosis. In FNAC, 65% patients had Fibroadenoma, 20% patients had Fibroadenosis and 6% patients had cyst.
Conclusion: Modified triple assessment is a very useful diagnostic tool to evaluate patients with breast lumps and to detect patients with breast cancers with an overall accuracy of 98%. Modified triple assessment was useful in diagnosing breast cancers at an earlier stage, with most of breast cancers detected at stage I or stage II (T1 or T2, N0 or N1, M0). It was found that triple assessment did not require hospitalization, but was performed on OPD basis, without any complications.
60.
The Effects of Contrast Medium Dose on Appendicolith Detection in Abdominal CT Scans: Hospital-based Research
Syed Arshad Hussain
Abstract
Aim: The aim of the present study was to investigate the impact of the amount of contrast material used in abdominal CT examinations regarding the diagnosis of appendicolith.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study that was performed to evaluate the diagnostic value of the CT examination in patients with acute appendicitis referred to Department of Radio-Diagnosis for 12 months. Two hundred patients that met the inclusion criteria entered the study using census method. Demographic data of patients including age, gender were obtained.
Results: In 70 patients, the CT scan findings were favorable for acute appendicitis, and the diagnosis was confirmed by the post-appendectomy pathological testing. Among the individuals undergoing CT scans, 5 false positive and 8 false negative results were recorded. The CT scan revealed that the patients had reduced peritoneal fat as well as a retrocecal appendix. The sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive value of CT scans based on pathology results were 88.6%, 82.8%, 95.5%, and 78.2%, respectively, in patients with low clinical suspicion. We evaluated the CT scan and ultrasonography based on the gender of patients.
Conclusion: In the clinical cases that there is suspicion of acute appendicitis, nephrolithiasis and ureterolithiasis, the present study recommends the acquisition of an abdominal CT applying however the following workflow. The CT protocol should apply first a low-dose pelvis CT scan in the region of cecum without contrast material. Subsequently, a second CT scan should be acquired with the use of oral and IV contrast.